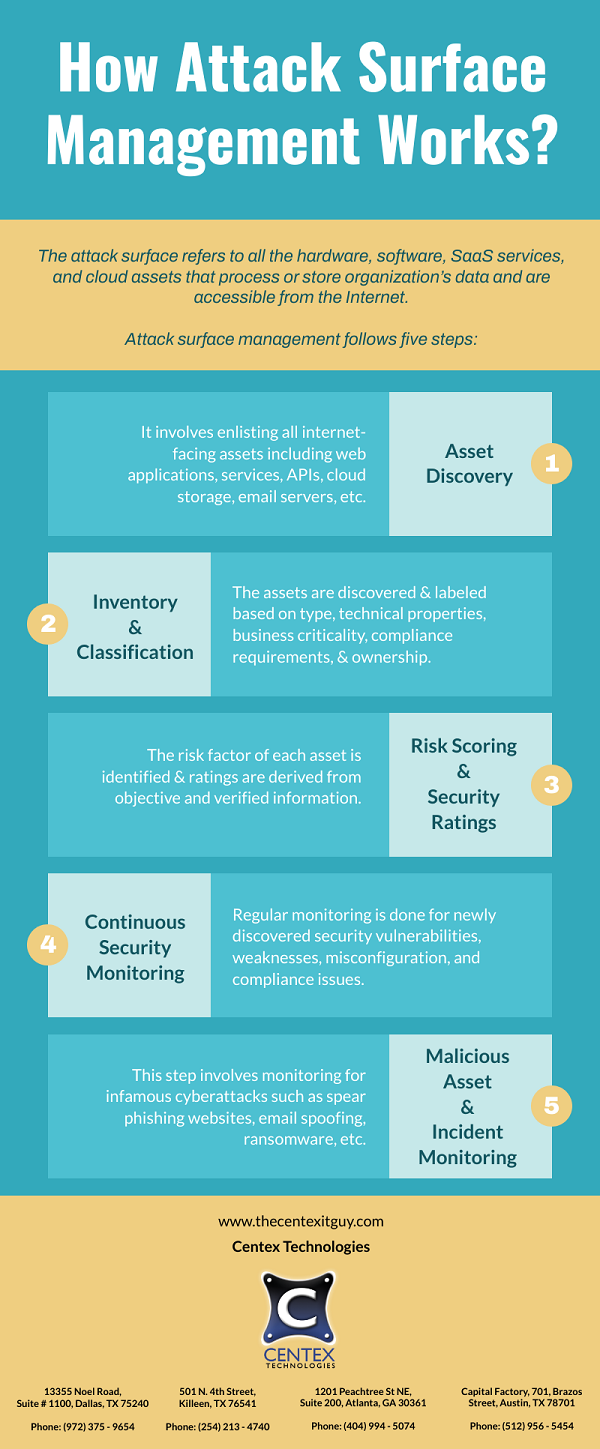
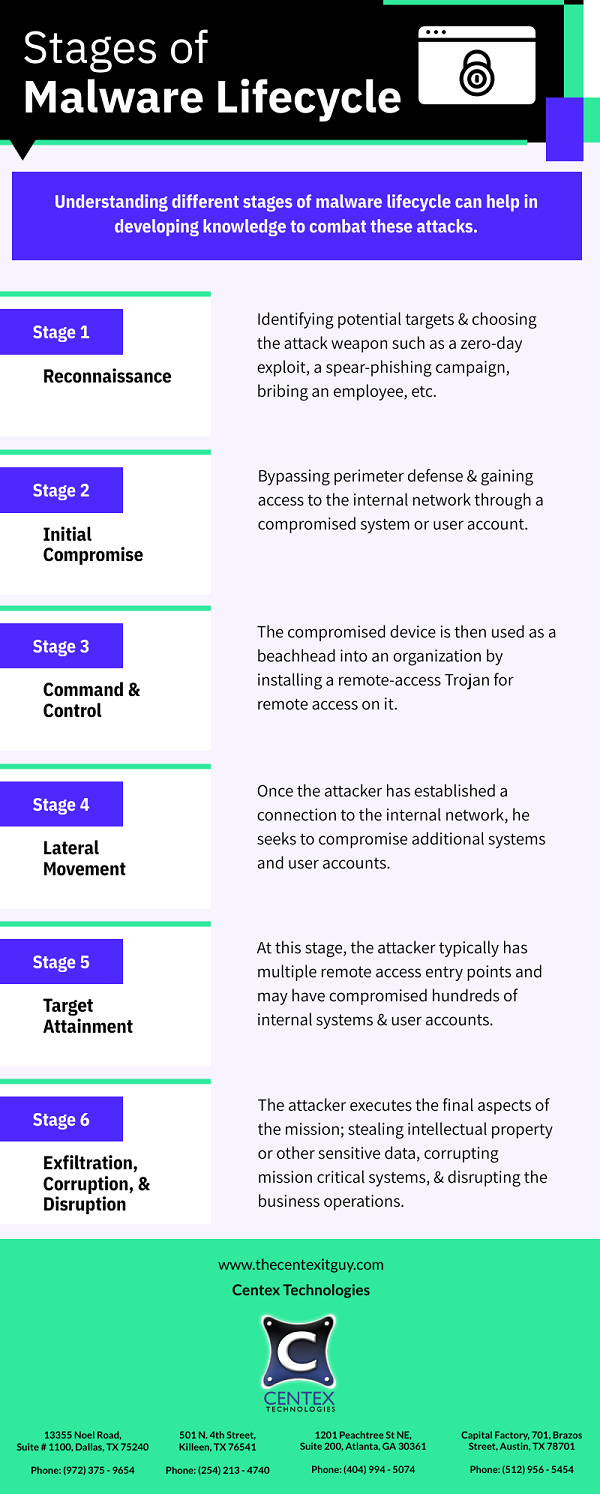
PDF Version: How-Attack-Surface-Management-Works
Most consumers believe that cyber risks only affect laptops or desktop computers. Mobile phones, in fact, have become the new focus of cyber assaults. The ever-increasing number of mobile phone users is a primary driver of this transition. Additionally, the enhanced capability of mobile phones has contributed to this transition.
The majority of mobile phone users nowadays use these devices to conduct most operations, such as making online payments, checking emails, storing personal data, connecting to their organizational network, and so on. As a result, mobile devices serve as a pool of opportunities for cybercriminals.
Another key factor that makes mobile phone users extremely vulnerable is a lack of knowledge about potential cyber security threats. The first step in addressing these threats is to get completely educated on the potential hazards.
Here is a list of some of the mobile security threats:
- Malicious Apps: Hackers frequently employ fake mobile apps with concealed malware and viruses. These programs are made to look like legitimate applications like games, instant messaging apps, or even antivirus software. The interface, including the layout, theme colors, fonts, and so on, is made to look like authentic apps in order to deceive mobile phone users into downloading false hacked apps. These apps, once downloaded and installed on a mobile device, can perform a variety of actions such as reconfiguring device settings, installing mobile ransomware, sending unauthorized communications, making social media posts, hacking user accounts, copying and sending personal photos to a third-party server, and so on.
- Mobile Greyware: This type of cyber-attack is less severe than a mobile virus, but it is more widespread. Mobile greyware refers to apps that do not include identifiable malware but can nevertheless harm the mobile device. These programs may be configured to control actions such as tracking the user’s location, monitoring web browsing history, boosting cell costs through unlawful internet access, and so on. ‘Madware’ or ‘Mobile Adware’ is a common type of mobile greyware. It may include apps that display unwelcome adverts in the notification area, substitute the call tone with a speech commercial, or disclose mobile data such as the contact list.
- Smishing: Smishing is a common term used for SMS phishing. It is a type of tactic used by hackers to target users via text messages. It is a preferred practice as it allows geographic targeting of victims. The fraudsters may pose as a local bank or credit union and send messages to locally present mobile users. The messages may include compromised links for stealing user information.
- Fake Networks: Similar to laptops or desktops, it is never a good idea to access an open Wi-Fi over a mobile device. Hackers can exploit these networks to intercept information such as emails, messages, login credentials, etc.
Centex Technologies provide complete IT security solutions for businesses. For more information, call Centex Technologies at (254) 213 – 4740.
The honeypot acts as a decoy, diverting hackers’ attention away from the real target. It may also be used as a reconnaissance tool, with the adversary’s methodologies, capabilities, and sophistication assessed through intrusion efforts. Any digital asset, such as software programs, servers, or the network itself, can be used to create a honeypot. It is carefully constructed to resemble a valid target, with structure, components, and content that are similar to the actual target.
Honeypot intelligence is important in assisting businesses in evolving and improving their cybersecurity strategy in response to real-world threats. It also helps in identifying possible weak spots in existing architecture, information, and network security. A honeynet is a collection of honeypots that are designed to appear as though they are part of a genuine network, replete with various systems, databases, servers, routers, and other digital assets. The cybersecurity team can track all the malicious traffic inside this isolated network while preventing the movement of the attacker outside.
Examples of Honeypots deployed in IT infrastructure
- False/apparent looking database: In this type of honeypot, a decoy database is created with a motive to mislead the cyber attackers. These databases include dummy information that resembles the actual database, however sensitive business information is missing from the decoy database. The honeypot database has some system vulnerabilities and weak system design, SQL injections, etc. These vulnerabilities pose as a soft target & attract the hackers.
- Spam honeypot: Spam honeypots work by accepting all the emails without filtering out the spam mails & other proxies. The program opens the mails to reveal their IP address of the spammers so that it can be blocked by the IT team for protecting the network systems.
- Fake email address: In this case, a fake email address is created which is not visible to legitimate users. The email address can only be reached by automated address harvesters. Thus, the cyber security team is not required to analyze every email and can rest assured that all the emails received on this address are spams and sent by cyber attackers.
- Spider honeypot: The motive of spider honeypot is to identify spiders – automated web crawlers. A net of web pages and links is created which is concealed from legitimate search engine web crawlers. Only automated and malicious web crawlers can access them. This helps in identifying how bot crawlers work to develop a way to block them.
- Dummy malicious software: A dummy software or an application programming interface (API) is created to attract the malware attacks. This helps in studying the vulnerabilities that are exploited and the techniques used by the attacker. The information is then used by the cyber security team to develop an effective anti-malware system.
Classifying Honeypots by their Complexity of interaction with hackers
- Low-interaction honeypots: This type of honeypots is not designed to behave like production systems but can be scaled, if needed. Although they fail to hold the attention of cyber attackers for long but are useful in causing a distraction for some time.
- High-interaction honeypots: These honeypots are more sophisticated and pose as actual network target. They have the capability to engage the cyber attackers for a longer period and are used to study the malware attacks to improve cyber security practices.
- Pure honeypots: Pure honeypots are full-fledged network systems and are designed with mock information, user data, etc.
Advantages of deploying Honeypots
- Recognizing threat actors: Since honeypot systems are only accessible to malicious actors, it makes it easier for the cyber security teams to identify and block them.
- Break down attacker chain: While the attackers might be crawling through your organization’s network, honeypots can be used to stop these crawlers and trap them from moving further.
- Adaptation and evolution of ML-AI algorithms: Honeypots assist in studying the mode of action of cyber-attacks and help in adapting ML-AI algorithms to protect against modern attacks.
- Insider & Outsider threat detection: Honeypots are unique systems that not only help in recognizing malicious actors but also insider attackers.
Risks
- Hackers might detect a decoy and try to deceive with fake intrusion attempts in order to divert the attention of SOC Analysts away from actual attacks on legitimate system targets.
- False information is conveyed to the honeypot by hackers to enable them to conceal their identities and confuse the detection algorithms and analytical models.
Honeypots are just one part of a larger cybersecurity posture. When used alone, the honeypot will not be able to safeguard the company from a wide range of dangers and vulnerabilities.
Centex Technologies provides cyber security solutions to businesses. To know more, contact Centex Technologies at Killeen (254) 213 – 4740.
Cyber security is a vast and dynamic domain. As new cyber security challenges emerge rapidly, it may become overwhelming for business organizations to keep up. To combat this, business organizations should implement a cyber- security checklist. A comprehensive cybersecurity checklist assists firms in adopting a cybersecurity-focused workplace culture as well as strengthening their cybersecurity posture for complying with various regulations.
1. Communications channels to be encrypted
Spam filtering technology in email servers automatically detects and eliminates emails that look to be phishing scams from employees’ inboxes. When communicating work-related information and passwords, use an encrypted email or messaging service to reduce the likelihood of the communication being intercepted and decoded. Employer-issued devices should never be linked to a public network. Also when viewing websites, employees should use security mechanisms and protocols.
2. Decentralize your cybersecurity strategy
Allowing the CISO to control and oversee user rights can help prevent specific departments from getting access to information they don’t need. Organizations that provide identical rights to all users are more prone to attacks.
3. IT strategies must be separated from Cybersecurity strategies
Cybersecurity threats are increasingly complicated and incident reaction times are more rapid. At the company level, the CISO should evaluate cyber threats and build mitigation and response plans.
4. Effective and efficient incident response process
An incident response strategy can assist staff in detecting, responding to, and recovering from cybersecurity problems with more efficiency. The incident response rules should be followed by all organizations. The strategy should spell out how to document and respond to cyberattacks.
5. End-user cybersecurity awareness training
A single mistaken click on a phishing email by distracted or anxious personnel might disclose vital information. Employees should be taught not to read emails from unknown senders or click links inside them. Leadership should be notified of any possible phishing assaults.
6. Implement ZTNA
The Zero Trust Network Access security paradigm is intended to instill in an organization’s culture a “never trust, always verify” mentality. By default, network administrators and IT employees are instructed to deny access to all devices in this cybersecurity architecture. Two-factor authentication is encouraged by a Zero Trust policy.
7. Strong and complex credentials
Passwords must be made up of a random sequence of alphanumeric and special characters. Also, store encrypted passwords only.
8. Automated updates and upgrades
Updates to operating systems are frequently applied to mitigate or eliminate vulnerabilities in older versions. Malicious software created for a certain version of the operating system will be discovered and deleted by the operating system in a future update when devices are upgraded. Antivirus software may be programmed to update automatically whenever a new version is published, improving the likelihood of protection from malware and other sorts of cyber-attacks.
9. Data backups
Employees must be able to restore their data from previous save points if their hard disk has to be reset. IT department should be in charge of data backups, and backup logs and tests should be performed regularly.
10. Access to critical systems to authorized security personnel only
No employee should be able to make changes to the company’s network and devices’ system details and configuration. Security threats are addressed by reducing the number of network administrators. Auditing and removing accounts from employees who have transferred workstations or are no longer employed by the company is another great practice.
11. Activate automated locking features
This stops onlookers from seeing what is displayed on the gadget. Users can remotely access the computer when it is logged in, which is why it should not be used unless it is under the direct supervision of an employee.
12. Device disposal and data-purge
When sensitive data is no longer needed, it should not be discarded. To delete all data from the hard disk, it should be entirely formatted. Any linked data may be entirely retrieved via a SATA connection without the hard disk being physically destroyed. Before destroying the drive, make sure the data on it is backed up.
13. Periodic cybersecurity evaluations and assessments
To identify new hazards, systems and software should be reviewed regularly. Some upgrades may cause systems to malfunction or expose them to risks. When evaluating a network, it’s essential to talk to an impartial cybersecurity professional who can give knowledgeable suggestions.
14. Employ 3rd-party security services
Leaders across organizations are advised to leverage the services from MSSPs (Managed Security Service Providers) to strengthen the cybersecurity posture of their organizations.
Centex Technologies provides cyber security solutions to businesses and also assists in formulating cyber security strategies. To know more about cybersecurity, contact Centex Technologies at Killeen (254) 213 – 4740.