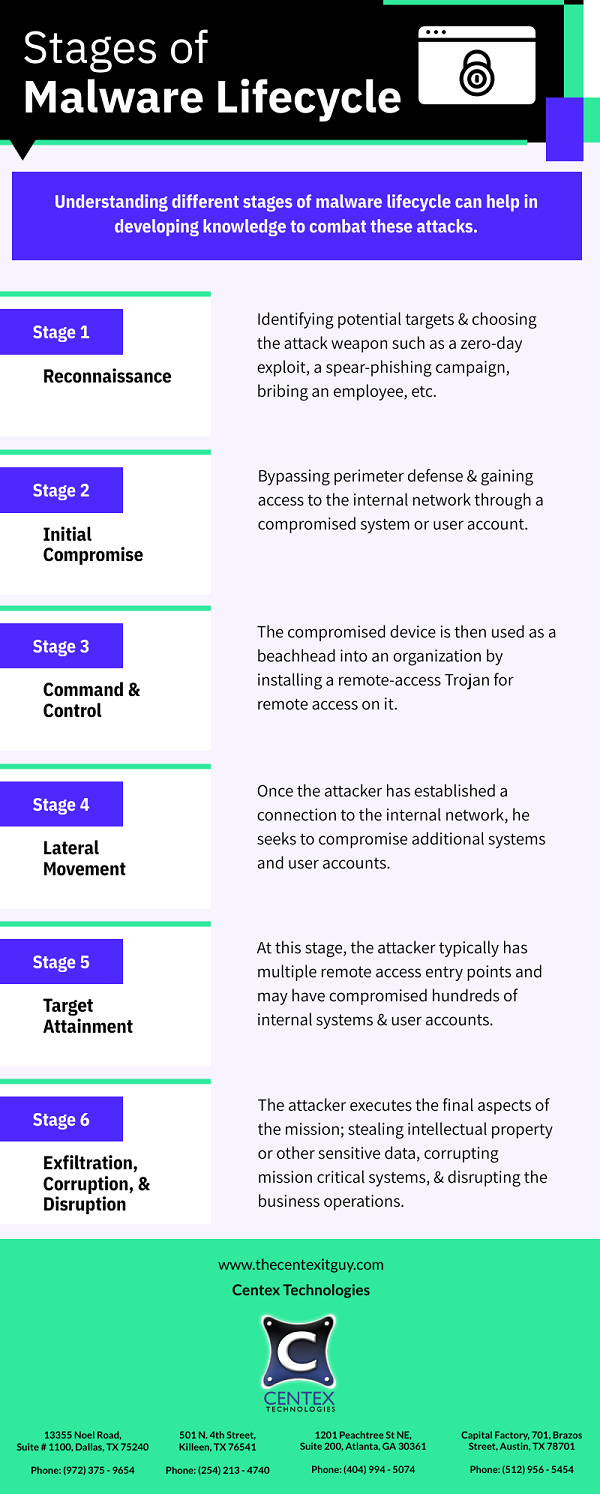
Spreading malware or virus across the network is a technique used by cyber attackers to spread their attack surface. By preventing lateral movement, organizations can limit the scope of a cyber-attack and minimize the damage caused.
Lateral movement cyberattack comprises the following steps:
- Initial compromise to gain access
- Reconnaissance to figure out the level of access and find targets
- Privilege escalation to gain a higher access level
- Lateral movement to infect targeted devices or apps
Preventing lateral movement is an ongoing and multifaceted effort that requires a constant focus on improving security measures to stay ahead of evolving cyber threats. Here are some steps to prevent lateral movement during a cyber-attack:
Limiting Access To System
The first step in preventing lateral movement is to limit access to critical systems and sensitive information. This can be done by implementing access controls, such as strong authentication mechanisms like Multifactor Authentication, and restricting user privileges.
Segmenting Networks
Segmenting a network prevents attackers from gaining access to other subnetworks. Segmenting can be done by implementing firewalls and routers to isolate different parts of the network.
Adopting Zero Trust
A Zero-trust architecture enhances security measures by assuming that any network traffic, whether internal or external, may pose a potential security risk. The system verifies and validates each access request which prevents system intrusion.
Network Traffic Monitoring
Monitoring network traffic can be done by implementing intrusion detection systems (IDS) and security information & event management (SIEM) solutions. These solutions can analyze network traffic, detect suspicious activity, and alert security teams.
Patching and Updating Systems
It is essential to regularly patch and update all systems and software to eliminate vulnerabilities that attackers can exploit to move laterally.
Implementing Least Privilege
By implementing the least privilege to user accounts, attackers will have limited access to systems and data, reducing the potential damage of a successful attack.
Using Endpoint Protection
Endpoint protection solutions (like antivirus/ firewall software) on all devices connected to the network can help prevent lateral movement by detecting and blocking malicious files and programs.
Conducting Security Audits
Security audits can help identify vulnerabilities and weaknesses in the network, and the results can be used to improve the security posture of the network and prevent lateral movement.
Training Employees
Employees should be trained on best practices for security, such as how to create strong passwords and how identify phishing emails.
To summarize, preventing lateral movement is vital for safeguarding against cyber-attacks. It’s crucial to adopt a comprehensive security approach and consistently assess and enhance the network’s security posture.
At Centex Technologies, we offer cutting-edge solutions to protect your business from evolving cyber threats. To know more about cybersecurity solutions, contact Centex Technologies at Killeen (254) 213 – 4740, Dallas (972) 375 – 9654, Atlanta (404) 994 – 5074, and Austin (512) 956 – 5454.