PDF Version: Security-Vulnerabilities-in-IoT-Devices
Tag: IoT Devices
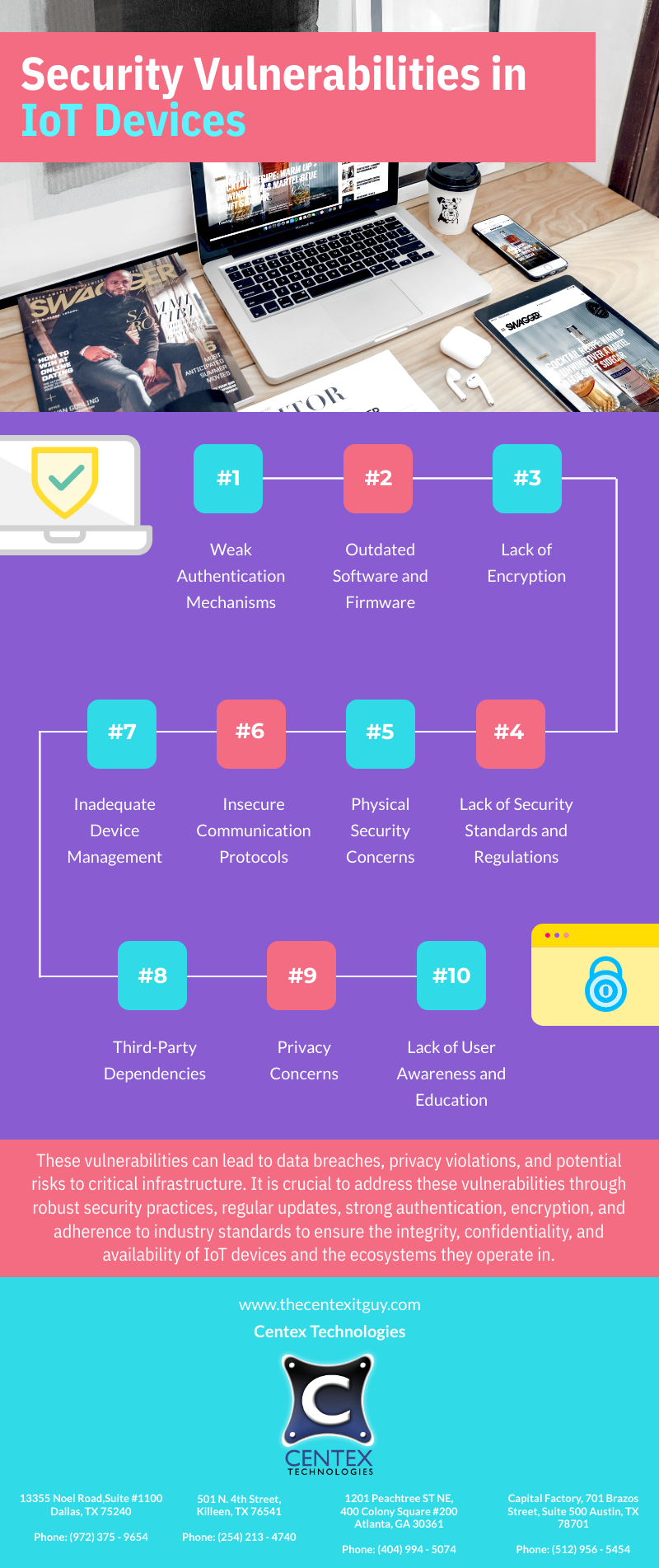
We have entered an era of smart devices where from washing machines, TV’s to refrigerators and AC’s everything is connected with the internet. As per reports by Cisco, the number of devices connected with the internet will exceed 50 billion by 2020. However, there are certain risks associated with IoT devices which every user must be aware of. Here we have listed some of them which demand user’s attention.
- Security Risks
There are a number of loopholes associated with IoT security, which a hacker takes advantage of. Security attack can be categorized into network, physical, software and encryption attack, each of which has its own consequences.
- Physical attacks target hardware of an IoT system and attackers physically harm the device to disrupt the services.
- Network attack on the other hand aims at disrupting the network layer of the device. DDoS attack is an example of network attack.
- Software attack is launched on the software with an intention to steal information & exploit the device.
- Encryption attacks target the implementation of algorithm on which the device works.
So, the user must possess thorough knowledge of the types of security risks and attacks to take preventive measures well in advance.
- Legal Risks
Legal issues related to product liability can arise. For example, if an autonomous car gets into an accident, who shall be held liable? Now this is a legal issue as it is difficult to figure out whether the owner, manufacturer, passenger or the person who coded the software is at fault.
- Privacy Risks
Since a lot of factors influence data protection, there are a variety of privacy risks associated with IoT. The number of cyber-attacks is soaring high and this has become a serious issue as nowadays most devices are connected to internet making it easier for cyber criminals to steal the information. This information can be applied to infer certain results or to be sold in the dark market which might be used against the IoT device user.
- Lack Of Authentication/ Authorization
A lot of vulnerabilities could lead to this issue. Lack of complex device password & two factor authentication, insecure credentials etc. are more like an open invitation to cyber criminals to hack the devices and disrupt the operations.
Other Risks
- Insecure Cloud Interface
- Complexity
- Insecure Mobile Interface
- Insecure Network Services
IoT devices now play a mainstream role in our lives, and have become a major part of our official & personal space. Thus, it is important to take a note of all the risks associated with IoT in order to understand the impact they can have on us. It is high time that we take necessary measures to mitigate the risks associated with IoT so that we can enjoy maximum benefits that technology offers us.
For more information about IT Security, call Centex Technologies at (254) 213-4740.
30th Aug 2017
Iot devices have given users a smarter control on various applications. These devices can connect and communicate with users and can be operated from almost any location in the world provided you have access to Internet. As IoT devices can be managed from remote locations, it is important to maintain their security and also of the network to which they are connected. The recent DDoS attack (of Oct 2016), which took down prominent service providers across US, is believed to be made possible by use of large number of unsecured IoT devices such as cameras, DVRs etc. So, security of IoT devices should be maintained, specifically to prevent such large scale DDoS attacks.
How to reduce the risk of DDoS attacks?
Use Of Unique Username And Password
A manufacturer should not rely on the end user for securing the device. A unique username and password needs to be set for the device along with a prompt to change these settings as soon as the device is powered on for the first time. The users also need to set strong passwords for the devices to avoid any kind of breach.
Protect Your Device And Servers
A number of monitoring functions should run on the devices to check for any kind of malicious activity from an unknown IP address. This will prevent the bot from accessing your internet and from repeatedly guessing the username and password. Make sure that you update your device and have its security analyzed regularly. Ensure that the server you are running, whether it’s your own or someone else, is secured and properly maintained. The data from the devices should be recognizable and difficult to spoof.
There are a few more things that can be done to prevent your devices from these attacks, which include:
- Users should turn off remote access to the IoT devices and limit the devices that can access your network.
- Get details of the network settings and its chain of communication with the devices from the connectivity supplier.
- The manufacturers should make sure that the device has sufficient DDoS mitigation capabilities.
- Users should learn how to scan their own networks for any security flaws. There are different tools which can
- help them in finding loopholes before the attackers do.
By securing the network and devices, the users not only prevent themselves from the potential DDoS attacks, but can also improve their device’s performance.
For network security solutions, contact Centex Technologies at (855) 375 – 9654.