Business-grade office networking solutions has crucial productivity, security, and functional characteristics that make the solutions a preferred choice for all enterprises. As the organization grows or there is an advent of newer technology, businesses should consider upgrading their office networks.
While upgrading their office network, businesses should invest in high-quality network equipment that features: –
- Intelligent Networking – Networks aided by RPA (Robotic Process Automation) and machine learning provide maximum performance on applications and services. The intelligent system can adapt, learn, and defend itself is an AI-enabled network.
- Multiple Wireless Network Support – A single wireless network is often supported by consumer access points. Multi-wireless networks, often known as SSIDs (Service Set IDentifiers), are supported by business-grade access points. This allows versatility and protection. Inbound-outbound rules, encryption, authentication, and other features can be applied to such SSIDs to provide an extra layer of protection. Additional dedicated SSIDs guaranteeing network isolation and congestion-free communications channel are formed for IP cameras and wireless speakers. Office owners can also utilize dual-band routers with 2.4 GHz and 5 GHz bands.
- NAS (Network Attached Storage) – A NAS is a data storage device. It’s a box with many hard drives configured in a RAID array to defend against hardware failures and faults. A network interface card connects directly to a switch or router and allows data to be accessed through a network. Data may be accessed using a shared drive from desktops, laptops, and servers. With NAS, there is no need to store copies of your papers on all of your assets and devices. It allows operators and business owners to deploy virtual computers and set up a media server that can stream to any device in real time.
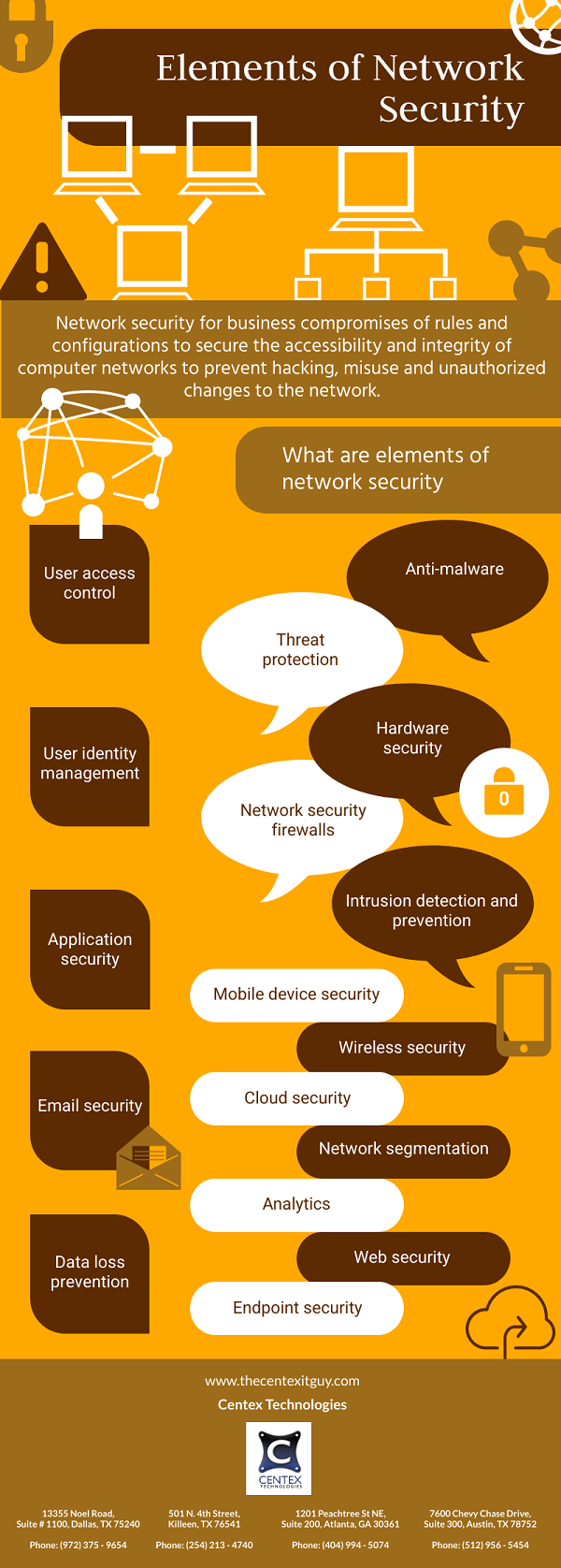
- Network Security – Physical network security is the initial layer, and it should keep unauthorized people out of physical network components. Access to network components must be logged, controlled, with mandatory biometric verification requirement. Technical network security is the second layer, which safeguards data in transit as well as data at rest. External threat actors as well as harmful insider activities can be mitigated implementing a VPN and/or two-factor and multi-factor authentication techniques. Antivirus and firewall software must be updated to only allow access to authorized staff. The administrative network security layer is the last layer, and it comprises of security rules and processes that regulate network user behavior. Unauthorized network access to specific applications and devices is limited by unified endpoint management.
- Cloud Computing – The distribution of services through the internet is referred to as cloud computing. Software, storage, analytics, and servers are all examples of internet services that are referred to as “the Cloud.” A cloud provider will host and keep the data for all of these services in the end. Access to applications, servers, and data is no longer restricted locally, making remote work easier. Threat actors finds it more difficult to infiltrate the network on the cloud. Both employees and the corporation benefit from a cloud-based network as they can utilize file sharing, screen sharing, and team messaging over the cloud network. When deciding on a team collaboration tool, compare the benefits and drawbacks of the vendor products shortlisted. Another advantage for employees is that cloud computing decreases the workload of the network administrators and allows them to focus on other activities.
Centex Technologies provide complete IT and computer networking solutions for businesses. For upgradation and for conducting an IT audit of office network, contact Centex Technologies at (254) 213 – 4740.